PCOS can cause problems with both infertility and recurrent miscarriages. Read on and discover the link between the two and what can be done about it.
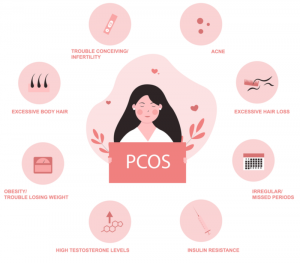
PCOS, also known as polycystic ovarian syndrome, is a common medical issue that can cause a range of health and other problems in a women’s life. The effects can be debilitating and can range from excess body hair and acne to recurrent and unexplained miscarriages. If you’re suffering from this condition, know you’re not alone: as many as 10 percent of women suffer from this condition.
What Is PCOS and How Does It Affect Fertility?
PCOS is a disorder that mostly affects hormones and the reproductive system in females. For many, it is a lifelong disorder that can only be managed with diet, exercise and sometimes medications. For others, lowering body fat percentage can help balance hormones and lead to a reduction in symptoms, if not entirely eradicating them.
Women who struggle with PCOS may not be aware they have the disorder. Symptoms vary widely, with some individuals suffering severe and debilitating symptoms and others having “silent” PCOS with no symptoms at all.
Common signs and symptoms of PCOS include but are not limited to the following:
- Irregular or infrequent menstrual cycles
- Lack of ovulation
- Excess body hair
- Acne
- Hair loss
- Weight gain/trouble losing weight
- Diabetes or pre-diabetes
- Skin tags
- Brown patches of skin
- Infertility
- Heavier than average periods
- Recurrent miscarriages
PCOS can affect fertility levels in a variety of ways. Too much testosterone, a symptom experienced by a majority of women with the disorder, can cause fertility issues like delayed ovulation or even anovulation, which is a complete absence of ovulation. Too much of this hormone may also play a role in PCOS-related pregnancy loss.
PCOS and Other Risk Factors for Recurrent Miscarriages
Recurrent miscarriages are sadly common among those who suffer from PCOS. A woman with PCOS has a much higher chance of miscarriage in general. While the average miscarriage rates among women hover around 20 percent, the rate climbs to 30 to 50 percent among those with PCOS. Even when undergoing fertility treatments like IVF, a woman with PCOS is twice as likely to have a miscarriage when compared to someone without.
Certain risk factors associated with the disease increase miscarriage risk. These include the following:
- Insulin resistance or elevated insulin levels
- Elevated luteinizing hormone levels
- Excess weight
- Elevated testosterone levels
These factors can also increase infertility rates. Some can be lessened through changes in eating habits or by adding exercise into your routine. In some cases, medications like Metformin may be used to treat PCOS symptoms like insulin resistance.
Can I Do Anything to Prevent Miscarriages?
In most cases, there’s nothing you can do to prevent a miscarriage. Some research shows that taking Metformin may reduce miscarriage rates. This is because elevated insulin levels have been linked to recurrent miscarriages.
For the most part though, it’s best to relax during your pregnancy. If the embryo has genetic abnormalities, a miscarriage may ensue. There’s nothing that can be done to change this. Know that if you’ve suffered through one or more miscarriages, there’s still hope. You can still go on to have a healthy and successful pregnancy, even after loss.
Though recurrent miscarriages are more common in women who suffer from PCOS, it doesn’t necessarily end your dreams of starting a family. With help from your team of healthcare professionals, lifestyle changes and possibly fertility treatments, you can get and stay pregnant. The road may be longer and more difficult, but it’s still one well worth traveling.