While many believe that morning sickness or food cravings are the most common events during pregnancy, it can actually also mean a miscarriage. About 30 percent of pregnancies are lost in the very early weeks of pregnancy.
Many women often lose their babies before even knowing they are pregnant. It is estimated that about 15 percent of women who have confirmed pregnancies lose their babies in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy. Therefore, it is important that pregnant women know their risk factors and symptoms so they can recognize signals that they could possibly be miscarrying.
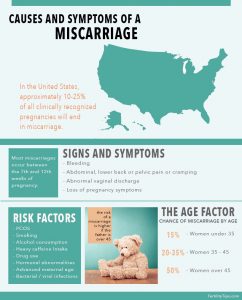
Causes of a Miscarriage
It is important for women who have miscarried to not blame themselves. Miscarrying a baby is not a result of moderate exercise, small doses of caffeine or sex. The most common cause is a random and chance chromosomal or genetic problem or abnormality in the embryo.
Some risk factors can be avoided, by pursuing a healthy lifestyle. This includes the renouncement of drugs, nicotine and alcohol. It also includes observing your diet choices and prevention of consuming foods that may contain listeria. Many other risk factors are unavoidable such as a car accident resulting in trauma, hormonal abnormalities, advanced maternal age, Lyme disease or a chronic illness.
Signs and Symptoms

However, some women have no symptoms at all during this process, as their bodies do not recognize the baby is not viable. These women may not find out what has happened until they go in for an ultrasound and the doctor does not find a heartbeat.
What Happens
The process of losing a pregnancy physically varies from person to person. Some women will begin to bleed and their uterine muscles will cramp. This is the body’s way of pushing out the tissue in the uterus by having small contractions. The body may expel blood clots along with the tissue from the uterus. If this happens quickly, the process is typically finished by the body without any further trouble.
If a woman has not recognized she has lost her baby and she has not experienced any symptoms, a doctor can administer a drug to encourage the uterus to contract and expel its contents.
A surgical procedure, called a dilation and curettage may also be done to expel the fetus. This surgery is done quickly so the mother is not at risk for health complications. The dilation opens the cervix if needed, and curettage then uses surgical tools to remove the contents of the uterus.
Recovery
The body itself heals very quickly after this process. A woman will generally begin normal ovulation within two to four weeks following the event. A normal menstrual period will then typically happen two weeks following ovulation. At this point, a woman can start trying to get pregnant again, with no additional risks to her health.
However, while physical recovery may be easy, emotional recovery may be more difficult. A woman is likely to feel very sad for a while. It is normal to be upset, and this intense sadness tends to diminish with time. It is important for women to allow themselves to grieve and even memorialize the loss of their child. Last but not least, a therapy can also help to overcome the loss.