Studies have shown that having a healthy circadian rhythm—and thus adequate levels of melatonin in the body—provides a healthy sleep-wake cycle.
Melatonin, a hormone released by the pineal gland at night, is most well-known for its role in eliciting sleep and helping balance the internal clock, or circadian rhythm.
New research finds that in addition to the sleep benefits of melatonin, it also is responsible for many different physiological processes in the body including healthy fertility and fetal development, thus playing a large part in men and women’s fertility.
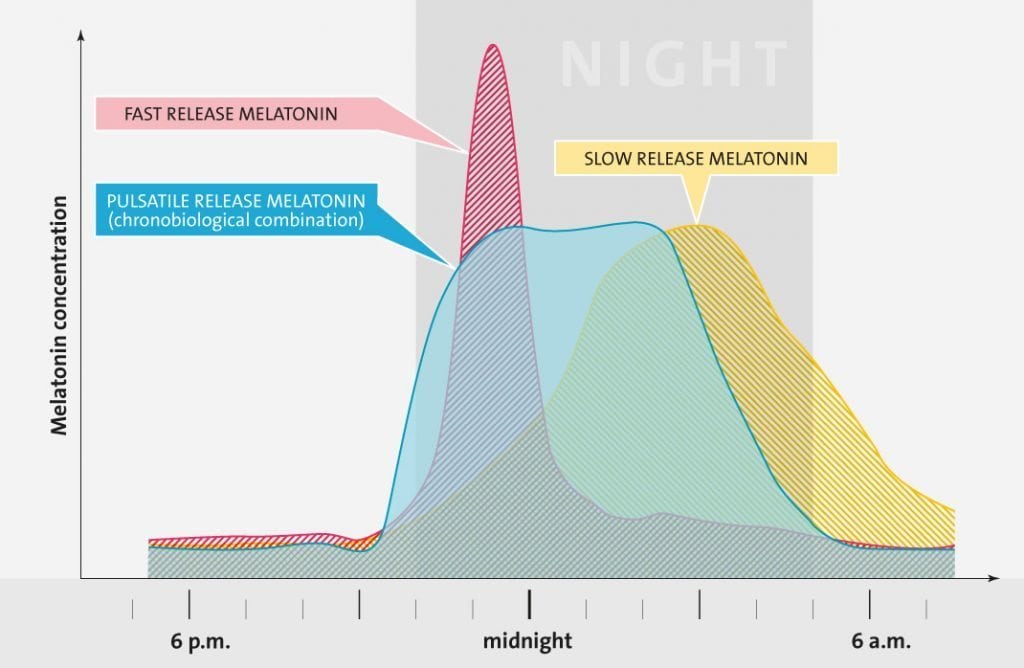
To benefit from Melatonin it should stay in your body as long as possible at night yet not make you tired during the day. Regular fast release Melatonin raises the Melatonin levels immediately, however, the half life is only 30 minutes which means half of the amount taken will be ineffective after half an hour. Slow release formulas increase Melatonin levels over a period of time, the downside, they create morning grogginess,
Therefore a pulsatile Melatonin formulation which raises the serum levels immediately, stay in the body over a period of time and then decrease fast is the optimal solution.
Melatonin for Fertility: How the Miracle Hormone Improves Male Fertility
About half of all infertility cases are due to the father. In the western world, sperm quality gradually deteriorates. The causes of this are manifold: Certain diseases, a genetic disposition and a series of negative lifestyle factors can significantly affect a man’s fertility.
Oxidative stress damages male sperm
Poor sperm quality is one of the main factors for male infertility. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the cell can lead to oxidative stress, which can attack male sperm. Seed cells are particularly at risk of being attacked by free radicals since they consist of a considerable amount of fat molecules. Reactive oxygen species can damage the cell membrane of the sperm, which limits mobility and impairs the fertilization. On the other hand, the DNA of the sperm can also be affected by ROS. If there is an imbalance in the body between the production of reactive oxygen compounds and antioxidative defenses, oxidative stress is the result. ROS and the resulting oxidative stress stem from external sources such as environmental pollution, drugs and negative lifestyle factors such as excess weight, nicotine and alcohol consumption, as well as certain medical problems. Leukocytes (which fight diseases) are another factor in the seminal fluid which produces high amounts of ROS. Men who experience excessive exposure to oxidative stress have a lower sperm count and more damaged sperm.
Melatonin as an effective antioxidant
Antioxidants are regarded as potent scavengers, as is the hormone produced by the human pineal gland that is released in the dark. Melatonin is able to directly intercept free radicals and render them harmless. Melatonin is localized, among other locations, in the mitochondria, where it improves energy production and counteracts reactive oxygen species. On the one hand, the hormone forms a defense against reactive oxygen species and combats free radicals by neutralizing them; on the other, it helps to build up healthy cells in the body and to support detoxification organs such as kidneys, liver and skin. Oxidative stress in the cell occurs when the physiologically normal levels of ROS are exceeded and the body can no longer sufficiently counteract it.
Melatonin and its influence on male reproduction
There are some studies that prove that melatonin has a positive effect on the reproductive function of men. For example, it has been shown that the hormone is located in the male seminal fluid and that it plays a decisive role in the defense against oxidative damage. In experiments with rats, melatonin was able to reduce the number of sperm with abnormal morphology and those with unstable DNA as well as to protect the testes from ROS.
The pineal gland hormone appears to be involved in some important processes, such as the protection of various cell types against damage-induced apoptosis (cell death). For example, in studies the protective effects of melatonin against apoptosis and antioxidative damage in ejaculated human sperm were reported, and the effect of melatonin was reported to be dose-dependent, with the highest dose being the most effective to prevent apoptotic events. These results suggest that stimulation with melatonin triggers a series of events culminating in cell death prevention in ejaculated human sperm.
Health of the testes
In several studies it was also documented that melatonin also directly influences testicular function. For example, melatonin receptors in testicular cells have been identified and the ability of the hormone to regulate testicular growth and testosterone production in testicular cells.
Melatonin also plays an important role in disorders of the testes, such as testicular torsion. This disease is often seen in infants and adolescents. The testis is twisted and the blood supply to the testis is cut off and ischemia occurs. Testicular damage associated with torsion is often associated with the production of reactive oxygen species. In a study with rats, it was shown that treatment with melatonin prevented damage resulting from a testicular torsion, resulting in decreased germ cell apoptosis, and increased expression of the proliferating nucleus antigen and production of testosterone.
Protection of sperm in artificial insemination
There are only a few studies dealing with the influence of melatonin on the in vitro storage of sperm. However, in some it could be shown that in sperm stored in a medium containing melatonin, the number of non-viable sperm was reduced and the number of mobile and fast cells increased. Especially in artificial insemination, it is important to protect sperm from ROS and from apoptosis during cryopreservation. It was shown that artificial insemination results are better when antioxidants are added. Melatonin can be used here as a powerful free-radical scavenger and as an anti-apoptotic agent to supplement sperm preparation media and to obtain a successful ART result.
Impaired fertility due to diabetes
In some studies, melatonin has also been shown to be helpful in men with diabetes who often struggle with reproductive problems due to the disease. Diabetes is a factor that is known to increase oxidative stress. People with type 2 diabetes tend to have lower daily melatonin levels compared to healthy people. In experiments with rats treated with melatonin, it was shown that the hormone counteracts some hyperglycemia-related complications by reducing oxidative stress and blood glucose levels and restoring the oxidative defenses. Melatonin also proved to be more effective than vitamin E, even in lower concentrations. Therefore, it can be concluded that melatonin plays a role in diabetes, a metabolic disorder that affects male reproduction. The effects of melatonin are also attributed to its highly antioxidant properties.
Influence of toxins on male sperm
Melatonin also plays an important role when it comes to counteracting damage to reproduction caused by toxins. These include endocrine disruptors (environmental hormones) such as BPA. In studies of mice, it was shown that in those rodents exposed to melatonin and exposed to BPA, the toxic effects could be reversed by melatonin reducing cell damage in the testes, restoring mitochondrial enzyme activity, and improving the antioxidative defense of testicular mitochondria.
In addition, melatonin has been found to be effective against the cell death of germlines induced by chemotherapeutic agents used in chemotherapy. Therefore, the hormone can be advantageously used in the treatment of impairments of the testicular function caused by these medications.
Although melatonin has proven to be helpful in the prevention and treatment of a number of male reproductive disorders, further studies are needed to investigate the exact mechanisms of action of the multifunctional hormone.
Lack of sleep
Just like female fertility, the fertility of the male can also be affected by a lack of sleep. Regular interruptions in the day-night rhythm, such as in shift work, have a negative effect on the melatonin production, which can impair reproductive capacity. A sleep deficit over a longer period of time can have a negative effect on male sperm. For example, studies have shown that men who sleep poorly reduce the sperm count by one-third and overall sperm quality suffers.
Therefore, men who are planning on fathering offspring should ensure good sleeping hygiene and eliminate negative lifestyle factors from their daily lives and, if necessary, add a supplement to increase melatonin levels and boost fertility in a natural way.
Melatonin for Fertility: How This Miracle Hormone Improves Female Fertility
Infertility affects many people. About every sixth couple has problems conceiving on the first try, and in about half of the cases, the problems attributed to the woman. The causes are multifaceted; one of the main factors consists of poor ovule quality. According to new scientific research, a hormone known as melatonin that is produced by the pineal gland in response to the dark can help with fertility problems.
Melatonin plays a key role in regulating circadian rhythms
Our bodies are subject to numerous rhythms that have to interact perfectly in order for our systems to function optimally. Next to a 24-hour rhythm and a seasonal rhythm, women also have a monthly cycle which controls fertility. If our internal rhythms and cycles get out of step, then numerous areas of our health are affected—including female fertility. Melatonin is a versatile hormone that has long been known for effectively regulating sleep, but it also has other positive effects on health that have been studied intensively since the ’90s. It helps control numerous hormones in the body and maintains our circadian rhythms.
Female fertility: A complex system
Female fertility is controlled through a complex system also known as the hypothalamo-hypophiso-ovarian axis regulates the release of several important hormones. The hypothalamus sends signals to the pituitary gland through a hormone known as GnRH. In turn, it reacts to the stimulation through the production of follicle stimulating hormones (FSH) and luteinizing hormones (LH), which then again stimulate the ovaries to produce estrogen and progesterone, which are hormones that trigger a number of physiological effects including egg maturation and ovulation.
Melatonin protects ovules
When talking about successful conception, healthy ovule production is essential. Both stable circadian rhythms, as well as appropriate melatonin levels, are decisive for the optimal functioning of the ovaries and the placenta. Melatonin is not only produced in the pineal gland but also in the reproductive organs, in the ovaries and ovules, in the cells surrounding the ovules and in the placenta. It helps to control the release of female reproductive hormones, as well as the quality of the ovules.
Melatonin is a potent radical catcher with anti-oxidant characteristics. Poor ovule quality is often induced by free radicals. If these gain the upper hand in the body, then they can damage the ovules. Melatonin defends against these aggressive oxygen compounds that are known to lead to oxidative stress in the cell, and can occasionally prevent cell damage, specifically at the time of ovulation. It cannot only remove free radicals, but it can also support other anti-oxidants in their work. Studies were able to determine that administering melatonin during the time of conception significantly improved the chance of pregnancy.
Melatonin ensures higher pregnancy rates in IVF
Melatonin helps to optimize ovule quality through the significant decrease of the concentration of the harmful oxidizing agent 8-OhdG. High levels of 8-OhdG mean that the ovules are of poor quality. Studies have shown that women who are undergoing IVF and take melatonin have a better chance of pregnancy and are more likely to bring a healthy child into the world. To obtain these results women were administered 3 mg of melatonin per day for three months after which IVF treatment could occur again. The amazing result: 50 percent of ovules were inseminated successfully, whereas, in the control group of women who did not take melatonin, the pregnancy rate was at a mere 22.8 percent.
Melatonin has positive effects on fertility disorders
The maintenance of healthy circadian rhythms is essential for optimal fertility, as any disturbance can negatively impact female fertility. This includes factors such as jet lag and shift work, which lead to a shift in the sleep-wake rhythm. The result for the woman is often an irregular menstrual cycle and problems conceiving. Disturbance of circadian rhythms can lead to important hormones not being released in an adequate amount and to an interruption in melatonin production. Studies demonstrate that women who are employed in shift work demonstrate irregular menstrual cycles more frequently. Melatonin has an influence on the female menstrual cycle, primarily through its effect on the hypothalamus to release GnRH. This triggers a chain reaction that eventually reaches the ovaries. Studies were able to show that supplementing through melatonin can help to control the frequency and length of menstrual cycles, as well as to increase progesterone levels significantly. Progesterone is an important hormone that supports the endometrium in its preparations for the fertilized ovule. If too little progesterone is present, it can result in a luteal phase defect, which frequently leads to problems conceiving and repeated miscarriages.
Consistent periods of dark are important for the production of melatonin
In order for sufficient melatonin to be produced, darkness is required. This is why it is recommended that women who are trying to become pregnant get around seven to nine hours each night in the dark in order to maintain a healthy circadian rhythm and optimal melatonin levels. Artificial light after nightfall should be avoided as it interrupts the master clock in the brain and suppresses nightly melatonin levels. Additionally, sufficient sleep is important for fertility. Interrupted sleep patterns often lead to fluctuations in the reproductive hormones, which in turn limits fertility.
If the production of melatonin is disturbed, then a supplement may help to produce healthy melatonin levels and to naturally stimulate fertility.
You may also be interested in...
-
Recurrent miscarriages can be physically draining and emotionally devastating. In some cases, a miscarriage occurs…
-
In this article, we discuss how a reduced level of CD9 can negatively impact the fertility of…
-
Celiac disease is a widespread chronic disease in the US and Europe that persists for…