A medical procedure known as zygote intrafallopian transfer has been known to offer good success rates. This procedure could be helpful for couples with fertility problems, who want to fulfill their dream of having their own child.
Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer Defined
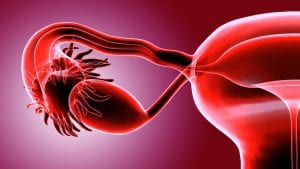
This procedure, sometimes referred to as ZIFT, is a fertility treatment that involves the implantation of a fertilized egg (embryo) directly into a woman’s fallopian tubes. From here, the fertilized egg then wanders down to the uterus, where, if successful, it will implant into the womb. This process all hopefully leads to a successful pregnancy.
Individuals Who Benefit From ZIFT the Most
ZIFT is performed on women eager to become mothers, but who have experienced conception difficulties. Fertility experts and medical professionals opine that the procedure is most effective for couples dealing with specific fertility issues including low sperm count and ovulation problems or in cases in which healthcare professionals cannot identify the reason for the couple’s conception challenges.
The ZIFT Process
ZIFT is a multi-step process that includes the following:
- Increased Egg Production – Women committed to undergoing the procedure ingest drugs designed to stimulate the ovaries’ production and retention of mature eggs.
- Follicle Development – During the egg-production phase, a recipient undergoes frequent, close monitoring of follicle development. Follicles are the structures where eggs mature for fertilization.
- Egg Retrieval – Upon completion of the maturation process, the physician performing ZIFT will examine the recipient’s ovaries and, with the aid of a needle-like probe, extract roughly 10 to 15 eggs.
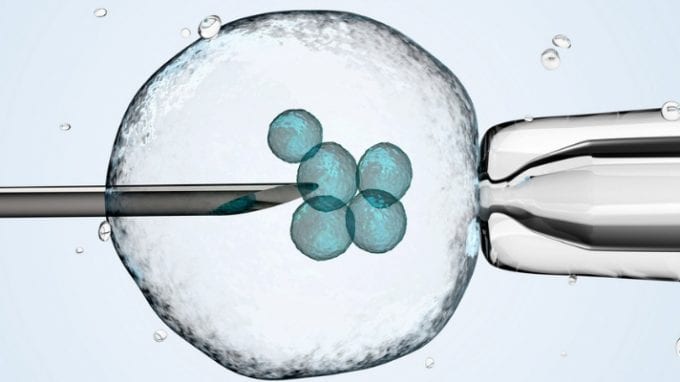
- Fertilization – Extracted eggs are then delivered to a specialist known as an embryologist. After examining the health of the specimens, the embryologist fertilizes the eggs using the sperm of the recipient’s partner.
- Zygote Formation – The fertilized eggs are housed in laboratory conditions and morph into zygotes within a day or so.
- Zygote Insertion – After the zygotes form, a surgeon makes an incision in the recipient’s abdomen using a laparoscope and inserts several of them into the patient’s fallopian tubes.
- Watchful Waiting – If the process is successful, one or more of the implanted zygotes will travel to the uterus, grow into a fetus and ultimately, a newborn child. In many instances, the results can be known within two or three weeks after the procedure has been completed.
 How ZIFT Differs From Other Fertility Treatments
How ZIFT Differs From Other Fertility Treatments
Though ZIFT shares certain principles with other fertility treatment options such as IVF and embryonic transfer, the procedure differs in that fertilized eggs are positioned within the fallopian tubes. During the other procedures, fertilized eggs are placed within the recipient’s uterus. Some women prefer this method, because they think it´s a more natural process than other forms of artificial insemination. This is because the fertilized egg travels down the fallopian tube and into the uterus on its own.
ZIFT Success Rates
Fertility experts and medical professionals caution that predicting ZIFT’s effectiveness can be challenging and depends on specific factors such as the recipient’s age, overall health, as well as the fertility-inhibiting issues the couple is facing.
Though younger women often stand the best chance for success, healthcare researchers estimate that the procedure increases a woman’s chances of becoming pregnant by more than 20 percent.
Possible Disadvantages
Prospective ZIFT candidates are asked to consider that the procedure is costly, might precipitate multiple births (such as twins and triplets), requires numerous steps that are somewhat time-consuming and involves surgery (whereas processes like IVF do not).
 How ZIFT Differs From Other Fertility Treatments
How ZIFT Differs From Other Fertility Treatments